
June 16

Fromelles Watercolor, 1915, by Hitler
1915 World War I: List Regiment: Gefreiter Adolf Hitler's 16 Reserve Infantry Regiment continues to occupy a position, at Fromelles, which is on a level field with water channels, willow trees and willow stalks, in the distance towards the enemy lines lie an insignificant wood with barbed wire entanglements. Under the direction of their defense-minded commander, Lieutenant General Gustav Scanzoni von Lichtenfels, the regiment works ceaselessly day and night to further fortify their position at Fromelles while fighting off repeated assaults by the enemy. [For further details, Click here.]
1916 World War I:Various:

Russian front: Brusilov, receiving little or no aid from the two other Russian army groups on the front, is battered by a German counteroffensive.
List Regiment: Gefreiter Adolf Hitler continues to endure trench warfare in Flanders (Artois) with 3 Company, 16 Reserve Infantry Regiment. [For further details, Click here.]

USA: President Wilson is re-nominated for president at the Democratic Convention in St. Louis, Missouri. Thomas R. Marshall is nominated for vice president. Wilson campaigns on the slogan 'He kept us out of war,' while skillfully preparing the way for entrance on the side of the Allies. (THP)
1917 World War I: Various:
List Regiment: Gefreiter Adolf Hitler's 16th RIR remains east of Douai for a period of rest, which will extend until June 24. [For further details, Click here.]
USSR: The first Congress of Soviets is convened in Russia.
1918 World War I: Various:
The Battle of the Piave River goes into its second day:
The Battle of the Piave River rages on the Italian front, marking the last major attack by the Austro-Hungarian army in Italy of World War I. [For further details, Click here]
List Regiment: (June 1-17): The 16th RIR hold the Front at Aisne and the Marne. [For further details, Click here.]
1932 Weimar: The Lausanne Conference opens for the revision of the Young Plan for German reparation payments. It is the first international economic conference since the crash of 1929, and due to worldwide economic conditions, its representatives agree to cancel all German reparations until better economic conditions return.
1933 Various:
Death: Ĥayim Arlosoroff: Zionist Labor leader:

Born in the Ukraine, Ĥayim Arlosoroff was taken by his parents to Germany in 1905 following a pogrom there. He went on to become a noted leader of the Labor Zionist movement in Palestine. While still in Germany, Arlosoroff had already become very active in Zionist affairs. In 1918, he co-founded Ha-Po'el haTza'ir, a party which attracted many intellectuals of the time. Later, when Ha-Po'el haTza'ir merged with Tze'irei Tzion, Arlosoroff emerged as one of the leaders of the new "Histadrut" (Union).
After his arrival in Palestine in 1921, Arlosoroff represented his party in the Histadrut. Soon after, he went back to Germany in order to complete his doctorate and returned to Palestine in 1924. In 1926 he was chosen to represent the Yishuv at the League of Nations in Geneva.
Arlosoroff was well-known for his particular ideological convictions. He vehemently disagreed with specific policies of his party and viewed prospects for unification of the Histadrut and Aĥdut haAvoda (another Zionist-socialist party) with skepticism. Despite his objections, Arlosoroff's party merged with ĥhdut haAvoda, leading to the creation of Mapai. Arlosoroff's voice was an important one amongst Mapai leaders.
Along with Ĥayim Weizmann, Arlosoroff supported the expansion of the Jewish Agency to include non-Zionists. He served on the expanded Agency's Administrative Committee, and continued to support other of Weizmann's policies. These policies included cooperation with the British government and understanding of the Arab position.
With the advent of Nazi Germany, Arlosoroff became a key player in the Ha'avara program, allowing the Jews of Germany to transfer some of their belongings to Palestine. He served as a link between German authorities and the Yishuv, facilitating Jewish immigration and settlement.
Ĥayim Arlosoroff was murdered in June, 1933, while walking on the Tel Aviv beach with his wife Sima. The identity of his attackers is the subject of much controversy, unsolved to this day.
Holocaust: German statistics for 'believing' Jews in the Reich, not including the Saar, are officially put at 499,682. (THP)
New Deal: The National Industrial Recovery Act becomes law. Note: It will later be struck down by the '8 old men' of the US Supreme Court.
1937 Various:
Holocaust: Poland:

General Lucjan Zieligowski in a speech to the Polish Senate declares, "there is no place in Poland for the Jews."
Church and Reich: The German People's Church (Deutsche Volkskirche) is accredited as the official Nazi church:

The movement rejected the universal nature of Christianity and had an abiding hatred for Roman Catholicism. Hopes to expand German Christian influence through supra-confessionalism were consistently dashed against the rock of German Catholicism and its ties to the Vatican. The People's Church began and ended at the German border.
Liturgists like Christian Wilhelm Bauer developed new rituals to provide experiences in communal self-affirmation while disguising the movement's doctrinal nihilism. Bauer wrote, "[Creation] of a genuine spiritual community depended on access to the irrational". He developed liturgies that blended Biblical language with fairy tales and myth, forming a syncretistic stew not altogether unfamiliar to American Catholics who have attended a liturgical workshop. Only those elements of Christianity that created a spirit of community found a place in the German Christian rituals. Hymns, including pseudo-psalms, were used to produce emotional involvement while suspending reason and judgment.
A lack of objective reality characterized the movement. While not submerged in the neo-paganism that pervaded both Weimar and Nazi Germany, the People's Church was influenced by the mythological and subjectivist spirit of the age. The historical resurrection became "a symbol of the resurrection within our own Volk ". Christian symbols and holidays were reinterpreted as expressions of the "spirit" of the Volk . Use of the cross was discouraged and Advent wreaths were re-interpreted. In short, Christianity was transformed from a religion based on the historic act of atonement to a ritual expression of Nazi ideology.
The People's Church, wholly engaged in building community, had little interest in the rights of individuals. The Sterilization Law of 1933 as well as the Euthanasia Program of 1939 met no German Christian opposition. On the contrary, Genetic Cultivation and Christianity was written to justify Nazi eugenics in German Christian terms.
At the end of World War II, the People's Church shouldered part of the blame for Germany's widespread capitulation to Nazism. Nonetheless, it was rapidly re-absorbed into mainstream German Protestantism. The history of this period, as well as that of the Weimar era which preceded it, merit close attention since, in some respects, it parallels our own times. When we hear appeals for an American democratic model to replace the hierarchical magisterium and "horizontal consensus" to replace the pope, we have to ask: Is horizontalism a neologism for collectivization pre-Nazi-style? It would seem to be a very short step from "The Church is People" theology to "The People's Church". Ideas have consequences: and they are not necessarily what we intend. [For further details, Click here]
1940 World War II:
France: Various:
German forces, supported by heavy artillery and Stuka dive bombers, continue their assault on the Maginot Line on a broad front.
Units of IXX Panzerkorps (Guderian) reach Besancon on the Swiss border.
The French ask Britain to be released from its obligation not to make a separate peace.
A British offer to establish a state of union between the two countries is rejected by the French.
Paul Reynaud is forced to resign as Prime Minister.
Marshal Henri-Philippe Pétain becomes premier of Vichy France:

As Germany began to overrun more French territory, the French Cabinet became desperate for a solution to this crisis. Premier Paul Reynaud continued to hold out hope, refusing to ask for an armistice, especially now that France had received assurance from Britain that the two would fight as one, and that Britain would continue to fight the Germans even if France were completely overtaken. But others in the government were despondent and wanted to sue for peace. Reynaud resigned in protest. His vice premier, Henri Pétain, formed a new government and asked the Germans for an armistice, in effect, surrendering.
This was an ironic position for Pétain, to say the least. The man who had become a legendary war hero for successfully repelling a German attack on the French city of Verdun during the First World War was now surrendering to Hitler.
In the city of Vichy, the French Senate and Chamber of Deputies conferred on the 84-year-old general the title of "Chief of State," making him a virtual dictator—although one controlled by Berlin. Pétain believed that he could negotiate a better deal for his country—for example, obtaining the release of prisoners of war—by cooperating with, or as some would say, appeasing, the Germans.
But Pétain proved to be too clever by half. While he fought against a close Franco-German military collaboration, and fired his vice premier, Pierre Laval, for advocating it, and secretly urged Spain's dictator Francisco Franco to refuse passage of the German army to North Africa, his attempts to undermine the Axis while maintaining an official posture of neutrality did not go unnoticed by Hitler, who ordered that Laval be reinstated as vice premier. Pétain acquiesced, but refused to resign in protest because of fear that France would come under direct German rule if he were not there to act as a buffer. But he soon became little more than a figurehead, despite efforts to manipulate events behind the scenes that would advance the Free French cause (then publicly denying, even denouncing, those events when they came to light).
When Paris was finally liberated by General Charles de Gaulle in 1944, Pétain fled to Germany. He was brought back after the war to stand trial for his duplicity. He was sentenced to death, which was then commuted to life in solitary confinement. He died at 95 in prison. The man responsible for saving his life was de Gaulle. He and Pétain had fought in the same unit in World War I and had not forgotten Pétain's bravery during that world war. (History.com)
Foreign Minister Ribbentrop to German Ambassador USSR (Schulenburg):

Please reply orally to Herr Molotov's question as follows:
1. As Mackensen reported upon inquiry, he did not make such a definite statement as was reported by the Soviet Charge in Rome to the Soviet Government. He had, instead, stated during the conversation with the Charge that in his opinion Germany and Italy were agreed that the Balkans should remain quiet and that a settlement of the unsolved Balkan question could probably be brought about more easily and without the use of force after the war.
2. The Reich Government was gratified that the war had not spread to the Balkans. Germany was, in principle, not interested there territorially but only commercially. Our attitude toward the Soviet Union in this question was finally and irrevocably established by the definite Moscow Agreement.
3. Italy's attitude toward the Balkans was also made unequivocally clear by Mussolini's speech on June 10 to the effect that Italy had no intention of drawing the Balkans into a war.
Baltics: The Red Army occupies Latvia and Estonia: Tens of thousands of 'hostile' natives and their families are rounded up and deported, separate from one another, to NKVD prison camps in the Soviet Union.
1941 World War II:

President Franklin D. Roosevelt orders the closure by 10 July of all German consulates in the United States.
[See: Why Did the US Eventually Join the Fight Against Hitler?]1942 World War II: Various:
From General Alfred Jodl's diary:

The Operational Staff of the Navy (SKL) applied on the 29th May for permission to attack the Brazilian sea and air forces. The SKL considers that a sudden blow against the Brazilian war ships and merchant ships is expedient at this juncture because defense measures are still incomplete, because there is the possibility of achieving surprise, and because Brazil is actually fighting Germany at sea.
War at Sea: The British light cruiser Hermione is sunk by U-205 (Kptlt. Reschke) South of Crete in the Mediterranean.
1944 World War II: Various:
Death: Marc Bloch: French historian of medieval France in the period between the First and Second World Wars, and a founder of the Annales School. Bloch's last book, Strange Defeat (published posthumously), was a brief assessment of the rapid failure of the French army to repel the German Blitzkrieg in 1940. Bloch was shot by the Gestapo during the German occupation of France for his work in the French Resistance.
Wunderwaffen: Another 244 V-1s are launched against London:
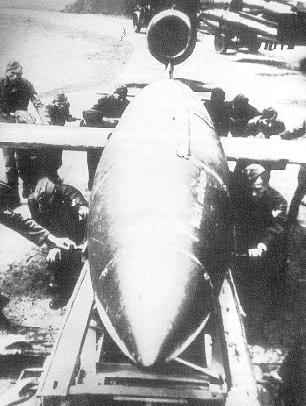
From Adolf Hitler by John Toland:
Hitler was still so convinced that the Normandy landing was a trick that he had not taken resolute action against this bridgehead, and by refusing to give his field commanders a free hand he had deprived them of thier last chance to seize the initiative. The battle was already lost. By now it was obvious that the Allies had won complete air supremacy over France, and Hitler turned to Goering, whom he had praised a few days earlier. He sarcastically asked whether it was true that his vaunted Luftwaffe had taken out a 'knock-for-knock' insurance policy with the West.
In desperation the Fuehrer inaugurated the V-1 rocket campaign against London on June 12, two days ahead of schedule. The harassed catapult crews could launch only ten flying bombs. Four crashed immediately, two disappeared, and the others destroyed a single railway bridge. After this fiasco Goering hastily reminded Hitler that this was Milch's program, not his, but when the second launching of 244 rockets two days later set disastrous fires in London the Reichsmarschall was quick to claim the credit. All this had no effect on the situation in Normandy. Within ten days the Allies had managed to land almost a million men and 500,000 tons of materiel.
From Albert Speer's SBS Interview:
V-2 cost approximately 20 times as much as V-1. The cost is very difficult to figure out for new production processes because there isn't a real mass production and the value factor cannot be calculated as yet. One V-2 used to cost one million marks in the beginning. I believe it then went down to 250,000–300,000 marks, but I don't want to quote any figures that I do not know exactly . . . . About 70,000 to 80,000 people worked on V-2, that is very much in proportion to the figures of 600 projectiles produced per month . . . .
It was difficult to procure the necessary amount of oxygen for industrial purposes. I found reasons against the expansion of this program. The bottleneck here was the electro-industry on one side, and oxygen on the other . . . . I had refused to produce more than 600 a month. Originally 900 were planned. I had also refused to carry out an initial expansion of the anti-aircraft rocket. I said that when the anti-aircraft rocket comes, V-2 will have to step back and its capacity used for the anti-aircraft rocket, because it was too great a luxury for me. I could have made about 5 to 6 Fighters with the same manpower as the V-2 took, which would have been better from my point of view. It is a technical experience to see such a rocket, piloted by a ray from below. That is technically the most advanced thing one can imagine . . . .
There was the danger that the projectile would not take off straight. Then one could observe the steering, how the projectile was always brought back into the right direction again . . . . As far as I know, a projectile came back (straight down) 10 or 12 times. But then there is none left in the neighborhood, except the command tank with the two people who guide the projectile. It happened that the fusing of the explosive charge did not immediately take effect, but only a few moments later, so that this last service crew could also get away. The worst thing was when the projectile could not be brought into the right direction, coming down approximately 30 kilometers from the launching site.

Eisenhower to Tedder:
With respect to CROSSBOW targets [V-1 launch sites], these targets are to take first priority over everything except the urgent requirements of the battle (Overlord); this priority to obtain until we can be certain that we have definitely gotten the upper hand of this particular business. (Eisenhower II)
Italy: The British Eighth Army under Alexander approaches Perugia.
1953 Spandau Prison: From Spandau: The Secret Diaries, by Albert Speer: Speer writes to his children in a letter that is smuggled out of Spandau:

Let me show you the kind of grave problems we have. Saturday, before the service, is our bath time, two of us at a time, as there are two tubs in the bathroom. As there are seven of us, the last has to bathe alone and that is usually me. Well, last week Funk asked me whether I mind if he went last—there is a Russian guard he can't stand who goes on duty at 11 AM and always makes a point of immediately looking in on the bathers, who at that time are usually Funk and Hess. I said fine, I'd bathe with Hess.
As it happened, I got to the bathroom just before Hess and got into 'my' tub; over the course of time we have come to feel proprietary about all kinds of things, among them the tubs. Hess comes in and asks, "What are you doing in my tub?" As you know, I am a peaceful man. "Oh, is this your tub?" I say and, with water pouring off me, get out of it and take the other. Hess bathes very quickly and is out while I'm still splashing about—you might send me a duck to play with next!
Funk comes in, ready for his bath, and makes a serious face. "What are you doing in my tub? says he. "That has been mine for six years." I know he is half joking so I burst quit laughing. "To punish you," he says, "I'm going to play nothing but Wagner at the service." As you know, he plays the organ—beautifully. And indeed, that was what he did . . . . Terrible, terrible Wagner, from Lohengrin to Gotterdammerung for forty-five minutes. Well, there you are—a look-in on our daily life.
Imre Nagy, a former Hungarian premier and symbol of the nation's 1956 uprising against Soviet rule, is hanged for treason by his country's communist authorities. [For further details, Click here.]
1963 First woman in space:

On June 16, 1963, aboard Vostok 6, Soviet Cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova becomes the first woman to travel into space. After 48 orbits and 71 hours, she returned to earth, having spent more time in space than all U.S. astronauts combined to that date. [For further details, Click here.]
1977 Death: Wernher von Braun:
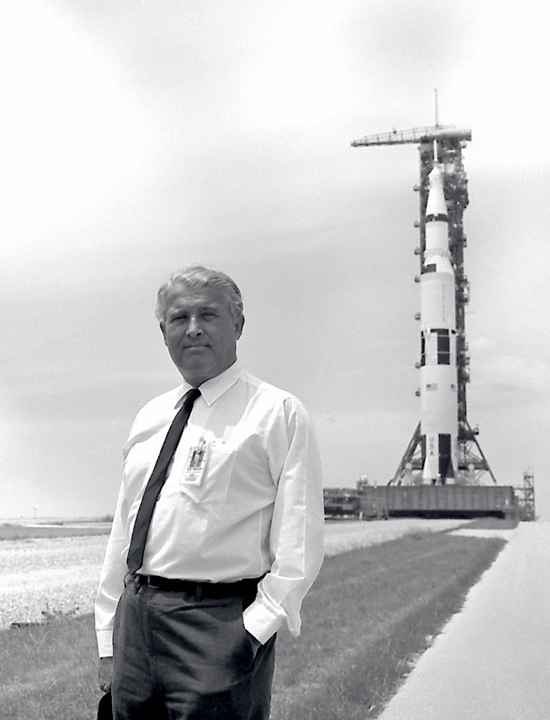

Von Braun was a rocket expert in Nazi Germany, an employer of slave labor, and was punished with the job of technical director of the US Army's Ballistic Missile Agency; later, the Marshall Space Flight Center; and in retirement, the vice-presidency of Fairchild Industries, an aerospace company. [For further details, Click here]
Edited by Levi Bookin (Copy editor) Click to join 3rdReichStudies Disclaimer: This site includes diverse and controversial materials—such as excerpts from the writings of racists and anti-Semites—so that its readers can learn the nature and extent of hate and anti-Semitic discourse. It is our sincere belief that only the informed citizen can prevail over the ignorance of Racialist "thought." Far from approving these writings, this site condemns racism in all of its forms and manifestations.
levi.bookin@gmail.com










Fair Use Notice: This site may contain copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. We are making such material available in our efforts to advance understanding of historical, political, human rights, economic, democracy, scientific, environmental, and social justice issues, etc. We believe this constitutes a "fair use" of any such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. In accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107, the material on this site is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. If you wish to use copyrighted material from this site for purposes of your own that go beyond 'fair use', you must obtain permission from the copyright owner.
Please Note: The list-owner and moderators of 3rdReichStudies are not responsible for, and do not necessarily approve of, the random ads placed on our pages by our web server. They are, unfortunately, the price one pays for a 'free' website.